LEARNING WITH UNDERSTANDING
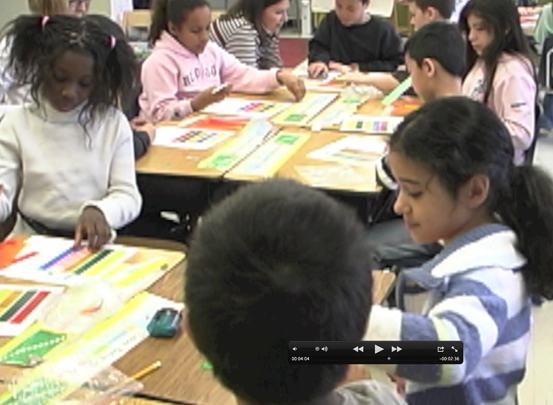
The major feature of the Fraction Bars program is the use of visual models to illustrate fraction relationships and operations before the use of rules and formulas. Activities with concrete materials provide opportunities for students to discover and discuss concepts and generalizations.
MAKING SENSE OUT OF FRACTIONS AND THEIR RELATIONS
The basic concept of fractions and equality and inequality are presented so that they make sense to students. Understanding and being comfortable with fraction numerals is the first and most important step. For example the numeral 1/8 means something is divided into 8 equal parts and sence only one of these 8 parts is being indicated the fraction is close to zero. Equality and inequality are introduced by comparing two bars to see if they have the same shaded amount or if one shaded amount is less than another. A fraction can be compared to 1/2 by just thinking about its numerator as compared to its denominator (or by thinking about the bar for the fraction). If the numerator is less than half of the denominator (or the bar is less than half shaded) the fraction is less than 1/2.
CONNECTIONS FROM WHOLE NUMBERS TO FRACTIONS
Fraction operations are presented in such a way that students can connect to their knowledge about whole number operations. For example addition means put-to-gether; subtraction means to compare two amounts or to take one amount away from the other. With fractions students are using a different type of number but the basic idea behind the operations is the same as for whole numbers. This is a connection that students seldom see in learning about fraction operations.
COMMUNICATION AND REASONING
Throughout the Fraction Bars program
students are talking and writing about the concepts of fractions. Before fraction notation is used
students are asked to verbalize or write statements describing what happens as they use Fraction Bars to model fraction concepts. In further steps
students continue to explain their reasoning through written and verbal description. As students get into the abstract levels of using rules and definitions for fractions
the models continue to be used in the lessons and activity sheets for the lessons.
PROBLEM SOLVING AND APPLICATIONS
Problem solving occurs in many ways in the Fraction Bars program. Word problems occur in many of the lessons
and three lessons are devoted entirely to solving word problems. The corresponding activity sheets in the Grades 3-4 Fraction Bars Teacher Resource Package for these three lessons also contain word problems.
GAMES FOR SPECIFIC FRACTION SKILLS
At every step of the way through the 3-4 grade teacher's guide
games designed for specific fraction concepts
and skills are described as part of the lesson. In addition
many of the 16 interactive games on fractionbars.com are referenced at the ends of the lessons.